Stereo Images¶
CameraTransform comes with a basic functionality to use stereo rigs. To calibrate a stereo rig, point correspondences in both images are needed. Stereo rigs should have two cameras that have different positions and orientations in space. We start with an example of two camera images:[1]:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
imA = plt.imread("StereoLeft.jpg")
imB = plt.imread("StereoRight.jpg")
Setting up¶
We assume that the internal parameters of the camera (lens distortion or projection) have already been obtained. We now start with creating two cameras that share the same projection and create a CameraGroup object of both.[2]:
import cameratransform as ct
cam1 = ct.Camera(ct.RectilinearProjection(focallength_px=3863.64, image=[4608, 2592]))
cam2 = ct.Camera(cam1.projection)
cam_group = ct.CameraGroup(cam1.projection, (cam1.orientation, cam2.orientation))
[3]:
baseline = 0.87
[4]:
cam1.tilt_deg = 90
cam1.heading_deg = 35
cam1.roll_deg = 0
cam1.pos_x_m = 0
cam1.pos_y_m = 0
cam1.elevation_m = 0
cam2.tilt_deg = 90
cam2.heading_deg = -18
cam2.roll_deg = 0
cam2.pos_x_m = baseline
cam2.pos_y_m = 0
cam2.elevation_m = 0
Fitting¶
To fit the relative orientations of the images, we need point correspondences. This is then added as information to the camera group.[5]:
import numpy as np
corresponding1 = np.array([[1035.19720133, 1752.47539918], [1191.16681219, 1674.08229634], [1342.64515152, 1595.28089609], [1487.18243488, 1525.87033629], [1623.55377003, 1456.86807389], [1753.39234661, 1391.94878561], [1881.18943613, 1331.92906624], [2002.45376709, 1275.17572617], [2119.63512393, 1220.46387315], [2229.46712739, 1167.79350718], [1132.21312835, 1106.84930585], [ 902.38609626, 1016.70756572], [1594.61961207, 628.61640974], [1794.85813404, 704.30794726], [1791.41760961, 663.70975895], [1956.56278237, 634.80935372], [2121.70795513, 600.40410939], [2288.22933766, 571.50370416], [2439.61241269, 544.66761359], [2583.42633397, 517.14341813], [2736.18561877, 488.93111778], [2876.55901561, 462.7831321 ], [3010.05136359, 437.3232513 ], [3144.23181646, 413.92768515], [3270.84311557, 393.28453856], [3393.32578537, 369.88897242], [2688.73357512, 1033.7464922 ], [2885.97789523, 1144.56386559], [3068.37586866, 1053.89510554], [2870.60132189, 952.09158548], [3237.51817542, 641.90898531], [3288.95016212, 879.98075878], [4105.49922925, 943.60795881], [3965.51938917, 692.28051867], [4037.41700677, 1135.08413333], [3253.6366414 , 1071.87603935], [3769.95210584, 1204.30954628], [4207.84687809, 1265.15387253], [3808.67122255, 1451.37438621], [3587.10046207, 1264.66938952], [3639.1604923 , 1353.23128002]])
corresponding2 = np.array([[ 352.50914077, 801.67993473], [ 460.08683446, 810.68133359], [ 570.95772285, 820.12182507], [ 682.48725018, 829.56231656], [ 797.35908021, 838.80579923], [ 908.18086062, 848.66284585], [1020.80811952, 858.76197628], [1135.19174893, 870.61747721], [1249.57537835, 882.03388552], [1365.71537827, 893.45029383], [ 911.70331034, 537.73870329], [ 956.46082091, 454.7508191 ], [1718.73717286, 432.37206381], [1706.61534708, 518.62351648], [2062.64027012, 573.54205381], [2203.84185338, 600.78475058], [2355.65939432, 631.55257909], [2518.58129093, 665.72644033], [2673.15840747, 699.10556061], [2837.669786 , 733.27942185], [3018.47335419, 768.64539453], [3202.45588621, 807.58770152], [3386.83578872, 844.9405266 ], [3584.72628753, 889.04864983], [3786.59049113, 932.3620321 ], [3991.63365858, 976.47015533], [2525.23601839, 1218.44516641], [2474.07408151, 1366.28811638], [2773.14569785, 1406.5405226 ], [2806.62667125, 1256.44042836], [3392.99303531, 1137.69520116], [2908.10263735, 1298.38150822], [3615.97183145, 1832.82274977], [4128.46912797, 1593.56296216], [3558.36872853, 2064.51618063], [2885.45082314, 1509.32652806], [3106.67717295, 1903.49557987], [3439.6617577 , 2276.44773767], [2628.22670423, 2051.78724561], [2789.70873377, 1806.36653735], [2665.39954766, 1885.90842814]])
cam_group.addPointCorrespondenceInformation(corresponding1, corresponding2)
[6]:
trace = cam_group.metropolis([
ct.FitParameter("C0_heading_deg", lower=0, upper=45, value=15),
ct.FitParameter("C0_roll_deg", lower=-5, upper=5, value=0),
ct.FitParameter("C1_tilt_deg", lower=45, upper=135, value=85),
ct.FitParameter("C1_heading_deg", lower=-45, upper=0, value=-15),
ct.FitParameter("C1_roll_deg", lower=-5, upper=5, value=0)
], iterations=1e6)
100%|████████████████████████████████████████| 1000000/1000000 [36:55<00:00, 451.28it/s, acc_rate=0.37, factor=0.00363]
[7]:
trace[::100].to_csv("trace_stereo.csv", index=False)
[8]:
import pandas as pd
trace = pd.read_csv("trace_stereo.csv")
cam_group.set_trace(trace)
[9]:
cam_group.plotTrace()
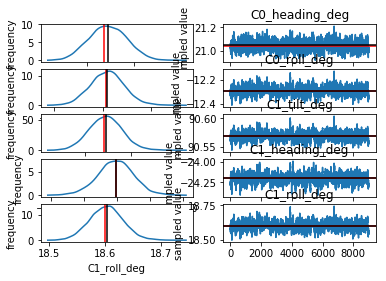
Measuring¶
This section will use point correspondences in a stereo rig to measure distances. We define the start points and the end points of the distances we want to measure in both images:[10]:
points1_start = np.array([[4186.75025841, 1275.33146571], [2331.92641872, 1019.27786453], [2001.20914719, 644.51861935], [1133.13081198, 1109.00803712], [ 900.20742144, 1016.83613865], [3287.47982902, 882.47189246], [3965.52607095, 693.78282123], [2689.04269923, 1033.94065467], [2889.82546079, 1144.44899631]])
points1_end = np.array([[3833.11271185, 1441.03505624], [2234.96105241, 1095.94815417], [2141.25664041, 614.81157533], [1797.43541128, 705.61811479], [1594.1321895 , 630.02825115], [4107.48373669, 942.87002974], [3238.54411195, 640.438481 ], [2868.55390207, 951.44851233], [3070.37430064, 1053.65575788]])
points2_start = np.array([[3390.15132692, 2262.6779465 ], [2312.57037143, 1067.65991742], [2112.03817032, 583.67614881], [ 910.64487701, 538.92782709], [ 955.7855831 , 454.96068822], [2907.87901391, 1297.11142789], [4125.81321176, 1596.76190514], [2524.07911816, 1219.84947435], [2472.59638039, 1365.81424465]])
points2_end = np.array([[2674.06029559, 2066.93032418], [2136.89506898, 1071.98893465], [2200.59552941, 598.28354825], [1706.9610645 , 517.94260225], [1718.87393798, 432.45627336], [3612.29928906, 1832.37417555], [3393.60277139, 1137.62004484], [2807.91089842, 1255.11024902], [2773.34835691, 1405.2303788 ]])
[11]:
points_start_3D = cam_group.spaceFromImages(points1_start, points2_start)
points_end_3D = cam_group.spaceFromImages(points1_end, points2_end)
distances = np.linalg.norm(points_end_3D-points_start_3D, axis=-1)
print(distances)
[0.13885105 0.04962405 0.03691601 0.21049065 0.21220163 0.21331054
0.21138547 0.07524718 0.0751257 ]
[12]:
# the first distance is known to be 14cm
scale = 0.14/distances[0]
# we use this ratio to scale the space
cam_group.scaleSpace(scale)